What is Ammonia (NH3)? Why use Vaporizer?
Idioma : English / Español

1. What is Ammonia? – Basic knowledge
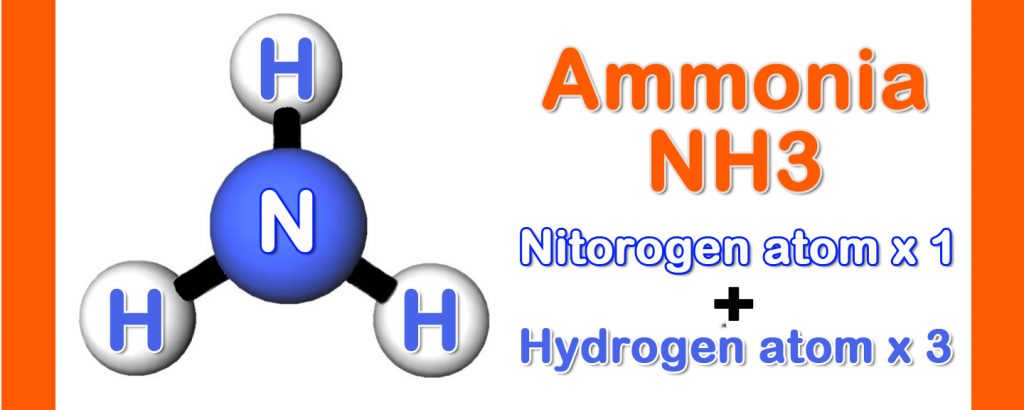
Ammonia (NH3) is a colorless gas with distinct odor. It is composed of single Nitrogen atom and three Hydrogen atoms. Boiling point of NH3 is -33.4℃. When vaporizes, a great amount of heat is absorbed.
Vaporization heat exchange of ammonia is the second largest after H2O. Compared to H2O that vaporizes at 100℃, ammonia generates a large amount of heat exchange at a low temperature of minus 33.4 ℃, and thus it is also used as a refrigerant. On the other hand, due to the large heat exchange of vaporization, if the heat source is not sufficient, vaporization becomes unstable and frost on the cylinder frequently occurs when gas is used for natural vaporization.
Ammonia, which does not generate CO2 when burned, has been attracting attention as a Green Gas in recent years, and more various uses are being studied.
2. What is the major usage of Ammonia?
Ammonia is seen in various field. It is a building-block chemical and a key component of many products including plastics, fabrics, etc. 80% of Ammonia produced is used for Fertilizer. More familiar use of ammonia is cleaning products for kitchen, bath, toilets and else.
And following are seen in the industries…
Refrigerant
- It is used as a refrigerant because it emits heat of vaporization next to water at minus 33.4 ℃
Energy Carrier for Hydrogen
- Hydrogen is attracting attention as carbon-free fuel just like Ammonia.
- Boiling point of Hydrogen is extremely low and thus liquefying hydrogen for transportation is a big task. While on the other hand, Ammonia with a high hydrogen density can be easily liquefied and stored.
**See “Ammonia Cracker” below for how to extract Hydrogen from Ammonia.
Fuel for Thermal Power Generation
- By co-firing fossil fuels and ammonia, CO2 emissions can be significantly reduced.
SCR(Selective Catalytic Reduction) / Nox Removal / Denitration
- Using ammonia as the reducing agent.
Metal Nitriding (Heat treatment / Thermal treatment)
- Nitriding is a heat treating process that diffuses nitrogen into the surface of a metal to create a case-hardened surface.
- Among several method of Nitriding, Ammonia is used for Gas Nitriding method.
Application example of Ammonia : METAL NITRIDING (METAL HEAT TREATMENT)
Operation image of Ammonia vaporizer for nitriding

Gas Nitriding is a heat treatment that infiltrates active nitrogen into the metal surface to increase hardness.
In this process, ammonia is flowed into the Nitriding furnace as atmospheric gas.
In the high temperature Nitriding furnace above 500℃, ammonia is decomposed into nitrogen and hydrogen on the steel surface, and the active nitrogen soaks into the steel surface.
Active nitrogen reacts with aluminum, chromium, etc. inside the steel to form a strong nitrogen compound.
In addition to hardening parts that require high hardness, such as metal parts used in automobile engines, it is also applied to surface coatings that prevent frying pans from burning.
Application example of Ammonia : AMMONIA CRACKER
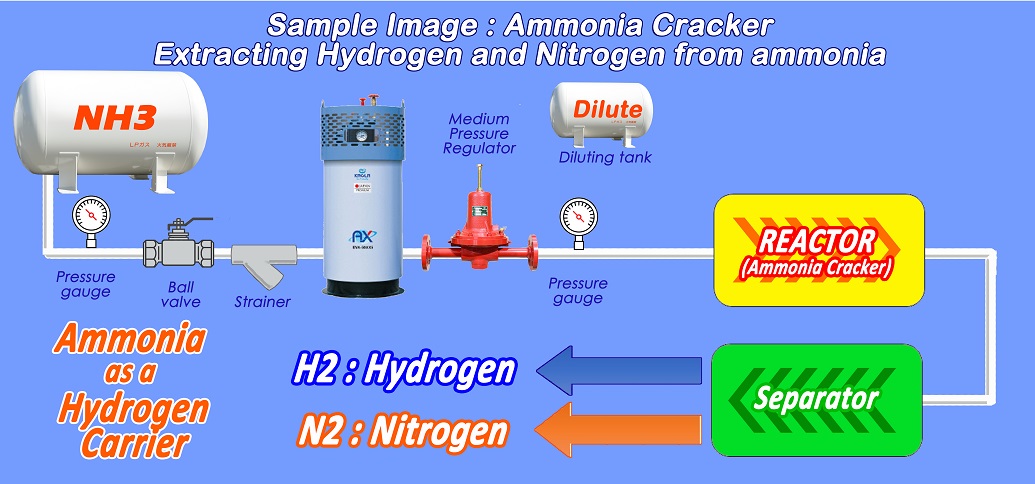
Ammonia as Hydrogen carrier : Ammonia Cracking technology to extract Hydrogen from Ammonia
As countries around the world advocate carbon-free clean energy, Hydrogen is attracting attention as a next-generation carbon-free fuel.
However, the storage and transportation of Hydrogen gas, which is not easy to compress and liquefy, is a major issue.
On the other hand, Ammonia, which also has carbon-free characteristics and can be easily liquefied unlike Hydrogen, is a gas composed of Nitrogen and Hydrogen in a ratio of 1:3 and is used as an easy and efficient Hydrogen carrier.
Ammonia Cracking is a technology that decomposes vaporized Ammonia gas into Nitrogen and Hydrogen with a high-temperature catalyst, making it possible to efficiently extract Hydrogen from liquefied ammonia gas.
Ammonia vaporizer is used to vaporize liquefied ammonia with high vaporization heat in a stable manner.
3. Negative Aspect of Ammonia
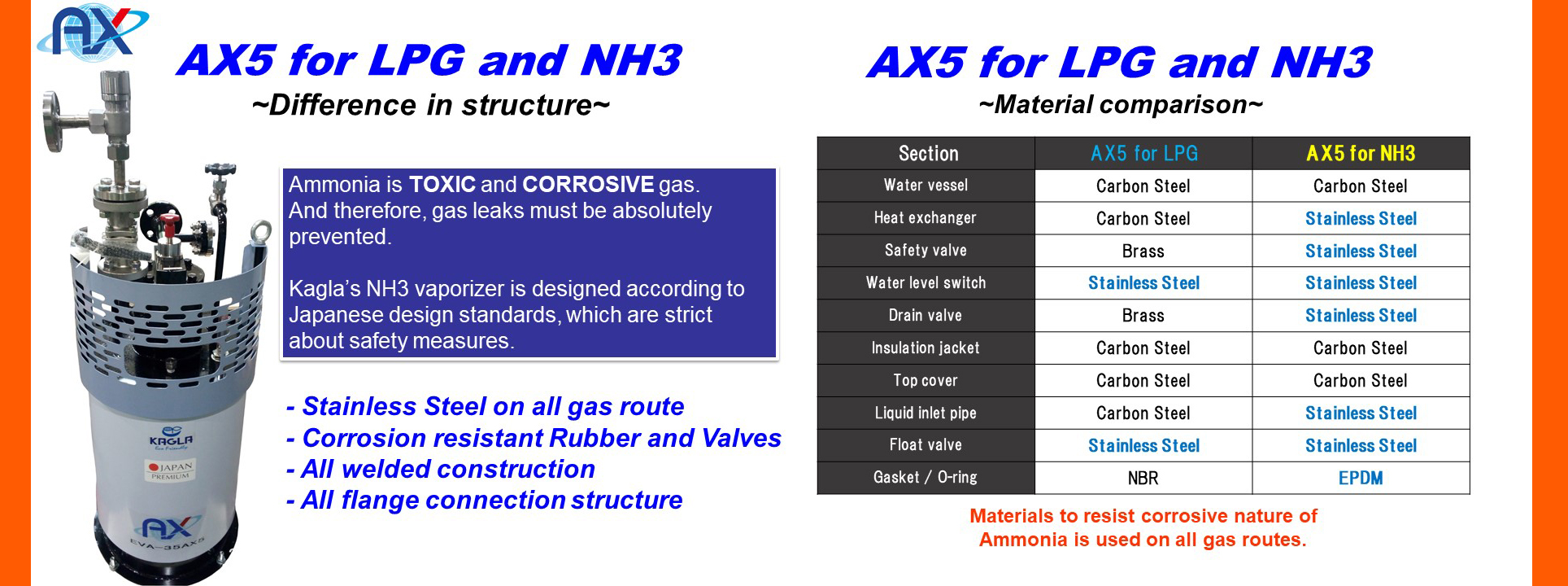
Ammonia is highly toxic and dangerous. And therefore it must be extra carefully to prevent gas leak.
Ammonia has alkaline properties and is corrosive. Valves, piping and the gas devices of LPG / NG cannot be used as they will be corroded. For safety operation of Ammonia, anti-corrosive material must be equipped.

4. Why do we need vaporizers for Ammonia?
Many of NH3 users take gas by natural vaporization from tanks / cylinders. If the consumption is not continuous and not in a large amount, this may be sufficient.


As mentioned above, Ammonia absorbs a large amount of heat when vaporizing. Therefore, if the heat source is not sufficient, vaporization becomes unstable and frost on the cylinder frequently occurs when gas is used for natural vaporization.
This picture shows frost on the Ammonia cylinder surface caused by too much heat exchange. When you see this, natural vaporization is not catching up with NH3 gas consumption. Vaporization is slowed down and thus Ammonia gas supply is not stable. You need to take some counter measurement or the business operation will be interrupted before long.
Temporally Solutions…?
Put the cylinder in the water or pour hot water on cylinder? Effective but not recommendable. This will induces rust on cylinder by exposing to water. Cylinder would be damaged afterwards… What if Ammonia may leak?
Heating the cylinder with fire? NEGATIVE!! Too dangerous!
These cannot be good solution…
AMMONIA VAPORIZER : Fundamental solution for Safe and Stable Ammonia gas supply
There are 2 other safer solutions against this problem of Ammonia vaporization.

Vaporizer enables stable vaporization of Ammonia gas anytime and thus it realize safety operation of business.
KAGLA’s Ammonia vaporizers are all designed in Anti-Corrosive structure. And the related Ammonia gas equipment are also available.